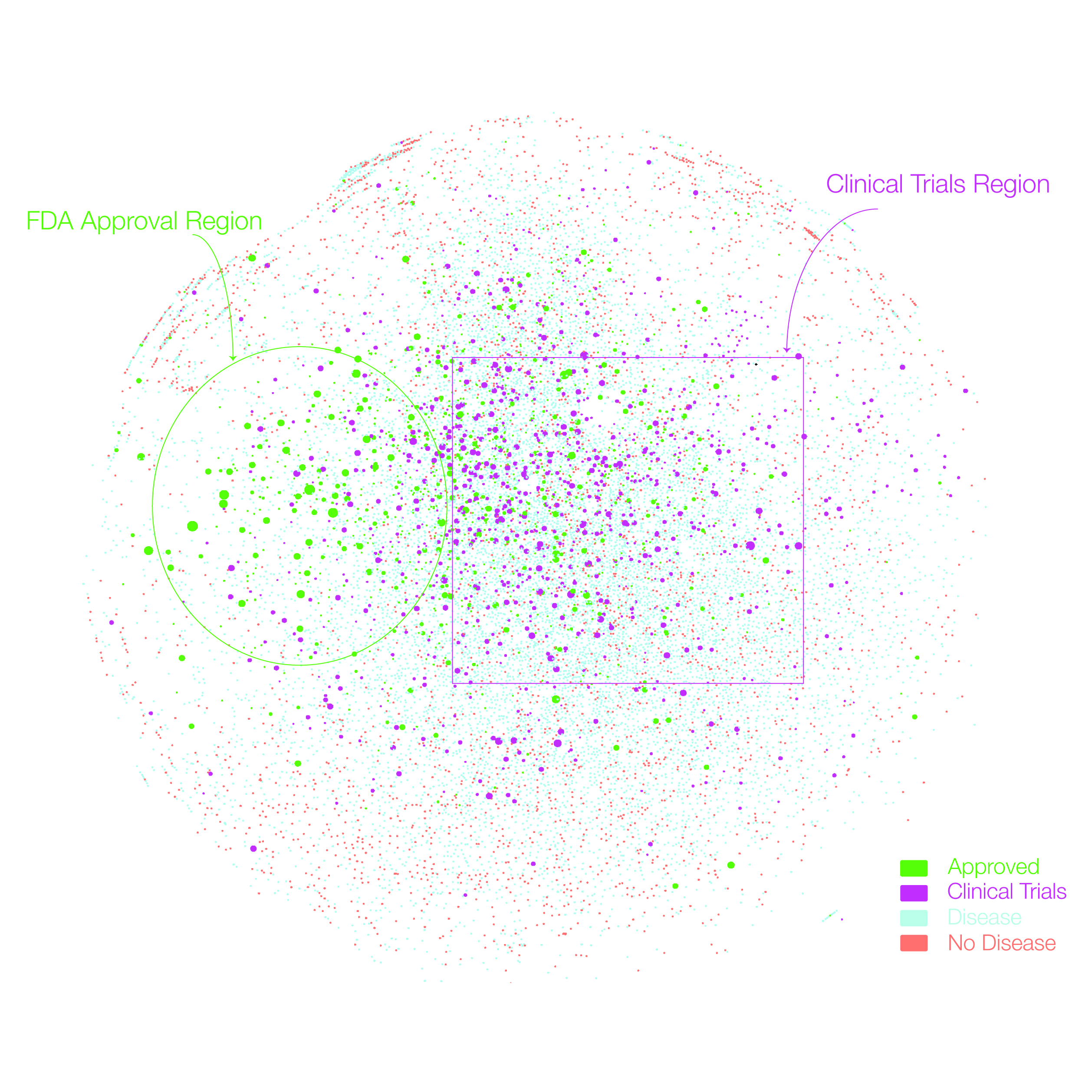
Given the functional interdependencies between the molecular components in a human cell, a disease is rarely a consequence of an abnormality in a single gene, but reflects the perturbations of the complex intracellular and intercellular network that links tissue and organ systems. The emerging tools of network medicine offer a platform to explore systematically not only the molecular complexity of a particular disease, leading to the identification of disease modules and pathways, but also the molecular relationships among apparently distinct (patho)phenotypes. Advances in this direction are essential for identifying new disease genes, for uncovering the biological significance of disease-associated mutations identified by genome-wide association studies and full-genome sequencing, and for identifying drug targets and biomarkers for complex diseases.
2012
Network Medicine & Biological Networks
About the project
Network medicine: a network-based approach to human disease
Tags
- network medicine
Related

PUBLICATION
Evolutionary conservation of motif constituents in the yeast protein interaction network

WORK
Drugging COVID

WORK
Diseasome

EXHIBITION
Spreading Phenomena and Virtual Networks














































































Contact
Social